Where a mechanical heat pump is driven by electric energy, an absorption heat pump is driven by thermal energy. This thermal heat is delivered by steam or by combustion of natural gas. Absorption heat pumps are very useful in situations where both heating and cooling is required.
The principle of operation of an absorption heat pump is based on absorption and evaporation of a refrigerant. An absorption medium as well as a refrigerant have to be chosen. Well known pairs are:
1. Litium-bromide (LiBr) and water, in this case water is the refrigerant and LiBr the absorption medium.
2. Ammonia and water, with Ammonia as the refrigerant and water as absorption medium.
Principle of operation
The figure on the right shows the principle of operation of an absorption heat pump. It is based on a heat pump that uses the pair Ammonia and water (NH3/H2O). The absorption heat pump consists of two loops. The loop on the right represents the absorption medium and the circulation loop at the left represents the refrigerant.
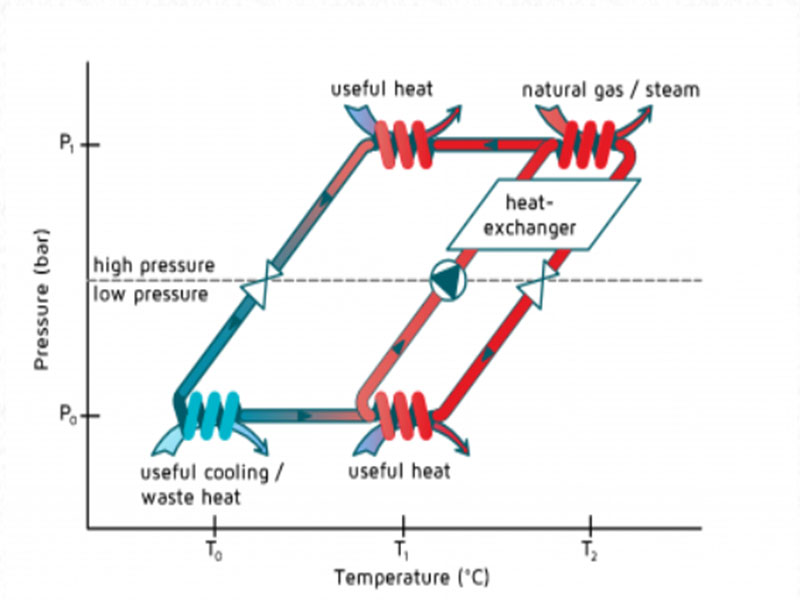
Cycle of the absorption medium
At the intersection of P1/T2, thermal energy is added to the generator of the heat pump. As a result the refrigerant is evaporated out of the absorption medium at high pressure. The absorption medium is lowered in pressure with the use of an expansion device and flows towards the absorber. Inside the absorber the gaseous NH3 is absorbed (intersection P0/T1). Due to the absorption process, useful heat is released at an intermediate temperature. The pressure of the mixture is than increased with a pump and flows back to the generator. To increase efficiency, an internal heat exchanger is used to preheat the cold mixture with the hot mixture.
Refrigeration cycle
At the intersection of P1/T2, thermal energy is added to the generator of the heat pump. As a result the refrigerant is evaporated out of the absorption medium at high pressure. The gas flows towards the condenser. Inside the condenser the NH3 releases heat to its environments and will condensate. The liquid Ammonia is than lowered in pressure inside an expansion device and flows towards the evaporator. At low temperature (at intersection point P0/T0) heat is added to the Ammonia and the Ammonia will evaporate. Waste heat can be used as heat source, but it is also possible to use the evaporator for cooling purposes. The gaseous NH3 than flows towards the absorber where it is absorbed in water. Due to the absorption useful heat is released.
Efficiency
Absorption heat pumps with natural gas as a heat source are commercially available. For the production of useful heat at a maximum temperature of 70 °C and cooling of the condenser with water or air, the efficiency is approximately 150%. In other words: the addition of 1 kWh of natural gas results in the production of 1,5 kWh of heat.
Remark:
Some of the articles are taken from the Internet. If there is any infringement, please contact us to delete it. If you’re interesting in heat pump products,please feel free to contact OSB heat pump. We are your best choice.

