Deciding to install a heat pump is a big decision to make for homeowner. Replacing the traditional fossil fuel heating system like a gas boiler with a renewable alternative is one that people spend a lot of time researching before committing to.
People will want to know things like what it’s like to live with a renewable heating system, how much they cost to install and operate, and whether to install an air source or ground source heat pump.
When carrying out research, the question may come up with to install a heat pump with an inverter drive unit or a fixed output. Depending on which manufacturer you’re researching, companies will have a preference one way or the other – usually influenced by the range of products they offer.
At Thermal Earth, we supply both fixed output and inverter heat pumps. We have over a decade’s worth of experience in the design, installation and maintenance of both types of heat pump systems, and we’ve seen first-hand how both inverter and fixed output heat pumps perform.
This knowledge and experience has confirmed to us, without doubt, that an inverter heat pump offers significant advantages in terms of:
· Higher overall annual energy efficiency
· Less likely to have issues with connection to the electrical network
· Spatial requirements
· The lifespan of a heat pump
· Overall comfort
But what is it about inverter heat pumps that makes them the heat pump of choice? In this article we will explain in detail the differences between them and fixed output heat pumps two units and why they are our unit of choice.
What is the difference between the two heat pumps?
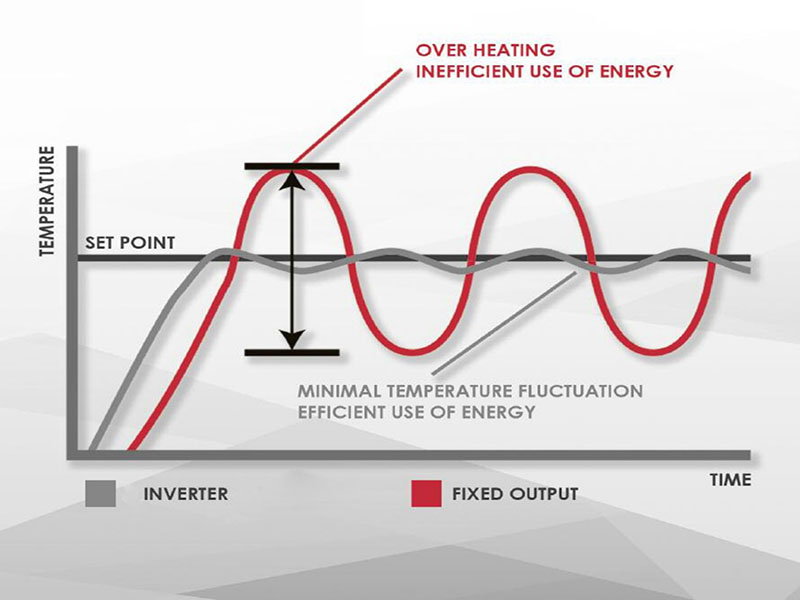
The difference between a fixed output and an inverter heat pump lies in how they deliver the energy needed from the heat pump to meet the heating demands of a property.
A fixed output heat pump works by continuously either being turned on or off. When turned on, the fixed output heat pump works at 100% capacity to meet the heating demand of the property. It will continue to do this until the heat demand is met and will then cycle between on and off heating a large buffer in a balancing act to maintain the requested temperature.
An inverter heat pump, however, uses a variable speed compressor which modulates its output increasing or decreasing its speed to match exactly the heat demand requirements of the building as the outdoor air temperature changes.
When the demand is low the heat pump will reduces its output, limiting the electricity usage and the exertion placed on the heat pump’s components, limiting the start cycles.
Remark:
Some of the articles are taken from the Internet. If there is any infringement, please contact us to delete it. If you’re interesting in heat pump products,please feel free to contact OSB heat pump. We are your best choice.

