Why should choose the air source heat pump to work?

Let go to learn how does the air source heat pump work?
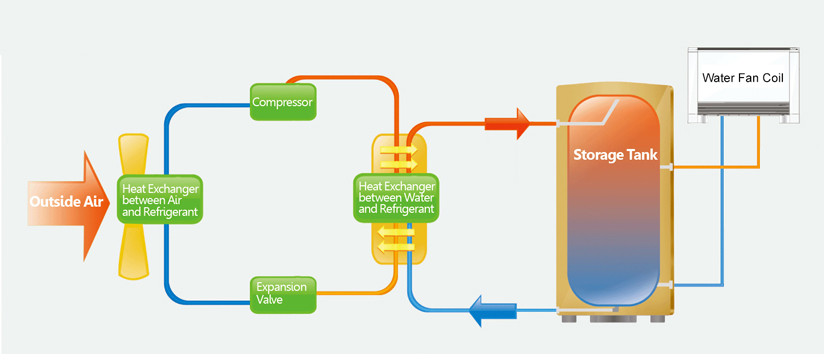
A heat pump is a device that transfers heat energy from a source of heat to what is called a heat sink. Heat pumps move thermal energy in the opposite direction of spontaneous heat transfer, by absorbing heat from a cold space and releasing it to a warmer one. A heat pump uses a small amount of external power to accomplish the work of transferring energy from the heat source to the heat sink. The most common design of a heat pump involves four main components – a condenser, an expansion valve, an evaporator and a compressor. The heat transfer medium circulated through these components is called refrigerant.
In heating mode, heat pumps are three to four times more effective at heating than simple electrical resistance heaters using the same amount of electricity. However, the typical cost of installing a heat pump is also higher than that of a resistance heater.
To refer the boiler and heat pump installation
Please refer these installation diagrams,you can see that are similar.
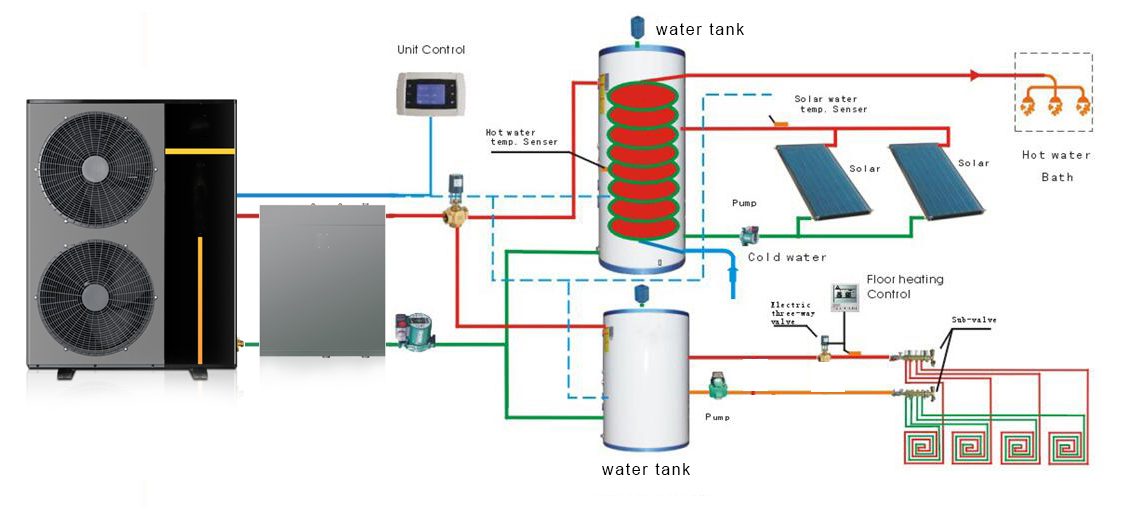
Heat pump installation diagram
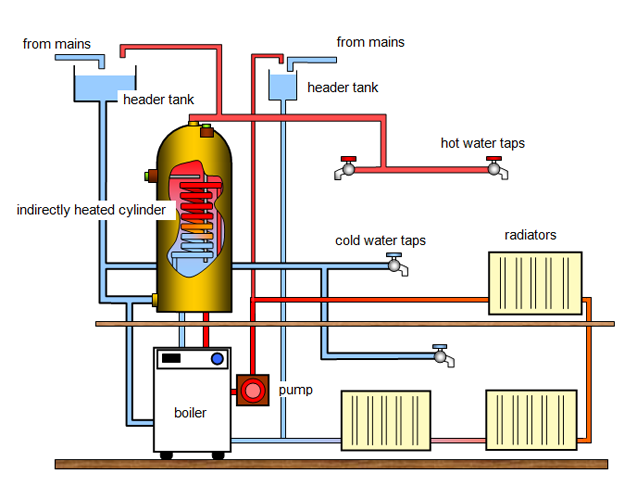
Diesel boiler installation diagram:
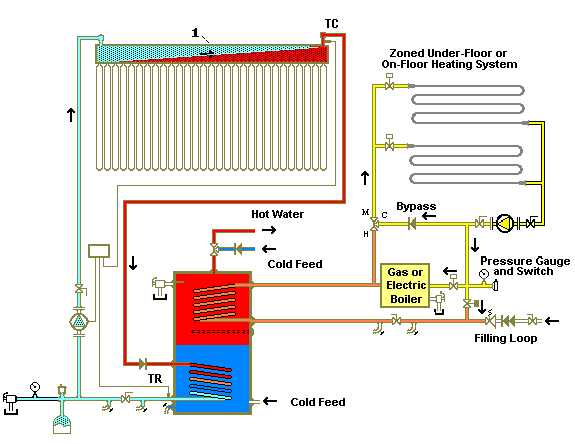
Gas boiler installation diagram
-----Why Choose The Heat Pump Rather Than The Boiler?----
1.The efficiency of a home heating system is essentially how much of the energy supply is converted into useful heat energy. Historically, old boilers are considered 50 – 75% efficient, which means that a half to a quarter of the energy supplied to the boiler was wasted. Modern high-efficiency boilers (gas, LPG and oil) and biomass boilers have a much-improved efficiency of around and above 90%, with only small amounts of heat lost through the flue.
2.On the other hand, the efficiency of heat pumps can, in effect, reach as high as 380% (or in technical terms, a Coefficient of Performance of 3.8). This is because heat pumps work by absorbing the heat occurring naturally outside of your home and moving it indoors.
1.A typical air source heat pump lasts for around 15 years, but allegedly newer models and ground source heat pumps have a lifespan of around 25 years. This longevity is put down to their robust design, and with only a few moving parts, there’s very little that can actually go wrong.
2.In comparison, a typical gas or LPG boiler’s lifespan is around 8 – 12 years.
1.While annual maintenance checks are advised for heat pumps, they’re not necessary. They can help to preserve a high efficiency and prolong life expectancy, but you can get away with not having routine checks without serious consequences.
2.On the other hand, it’s strongly advised that boilers have at least annual maintenance checks from HVAC professionals. This is to ensure safety, namely to reduce the risk of carbon monoxide poisoning.
1.Since both gas boilers and heat pumps are fully automated, the user experience will largely depend on the model you choose. As with most modern appliances, there are umpteen extra functions to improve ease of use, comfort and control. App-controlled systems, timers and programmable room thermostats are just a few of the functions we think are worth looking out for.
2.Unfortunately, a biomass boiler will require slightly more effort, as you’ll have to manually fill it with wood pellets each time. There are options to have pellets delivered to your door, but this will depend on a willing third party located in your area.
1.Despite the efficiency of gas, oil and LPG boilers rising to approximately 90%, heat pumps don’t burn fossil fuels to generate heat, making them the clear winners of this round. Their high efficiency also means that even if the electricity powering the heat pump was generated in a coal-fired power station, the carbon emissions given off would be minimal.
2.Biomass boilers are also a green heating option worth considering. As they burn wood, they’re only emitting the same amount of carbon emissions that were absorbed, so they’re technically carbon-neutral.
◪Heat pump vs boiler Round 6 – Heat Pump & Boiler Space
The outdoor fan unit of an air source heat pump usually takes up as much space as a washing machine. This is usually (but not always) connected to an indoor heat exchanger (or hydrobox), which is roughly the same size as a regular boiler. Finally, the hydrobox connects to a hot water cylinder, just like a regular gas boiler.
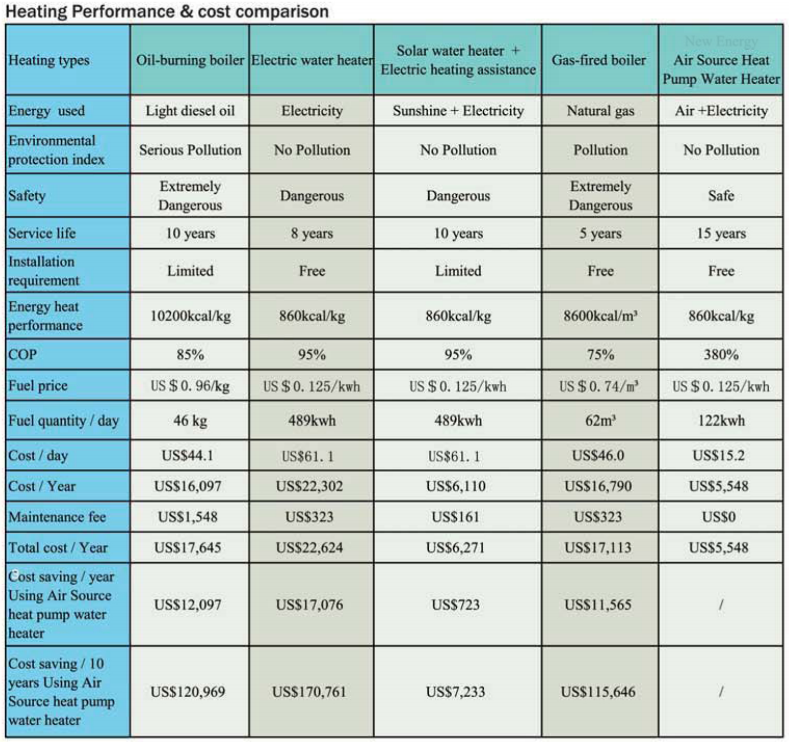
AIR SOURCE HEAT PUMP VS BOILER: 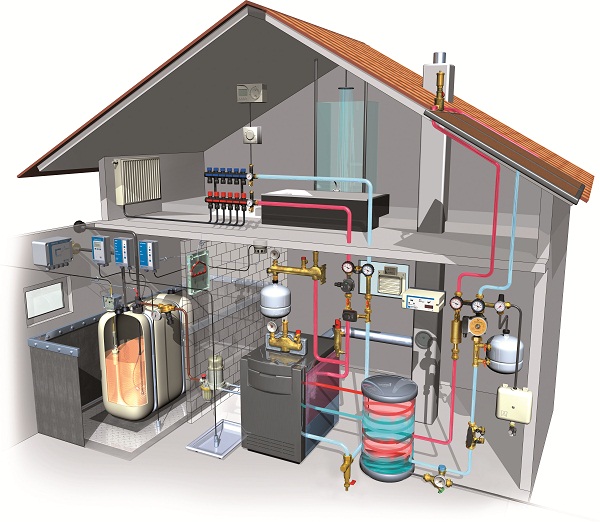
>No pollution >Not dangerous >Longer lifetime >Free installation >Higher COP >Don't maintenance

