The efficiency of refrigeration systems and heat pumps is denoted by its Coefficient Of Performance (COP). The COP is determined by the ratio between energy usage of the compressor and the amount of useful cooling at the evaporator (for a refrigeration installation) or useful heat extracted from the condenser (for a heat pump). A high COP value represents a high efficiency.
Most of the electric energy needed to drive the compressor is released to the refrigerant as heat. Therefore more heat is available at the condenser than is extracted at the evaporator of the heat pump.
For a heat pump a COP value of 4 means that the addition of 1 kW of electric energy is needed to have a release of 4 kW of heat at the condenser. At the evaporator side 3,0-3,5 kW of heat is extracted. The additional heat is generated by the compressor. On the other hand: For a refrigeration system a COP of 4 indicates that 1 kW of electricity is needed for a evaporator to extract 4 kW of heat. Due to this important difference in COP definition, for a heat pump one often speaks of CO Ph. In this abbreviation 'h' means heating.
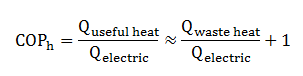
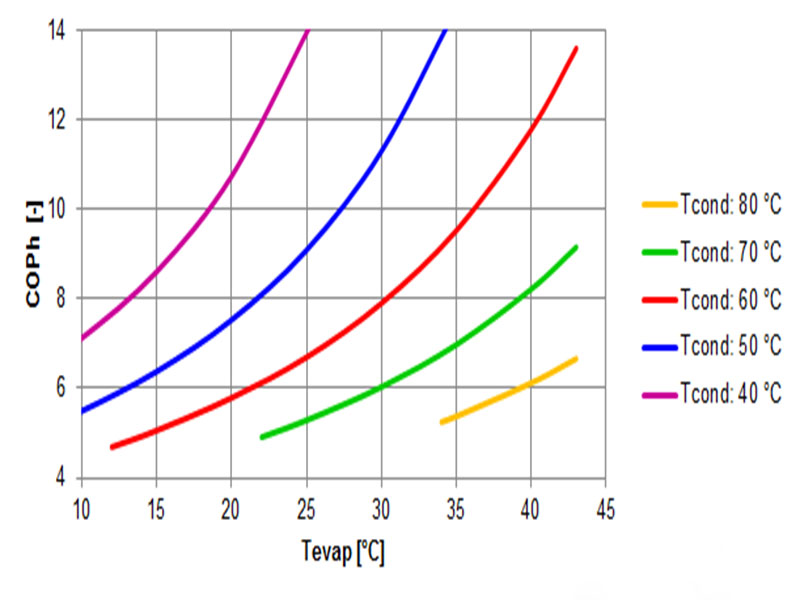
The efficiency of a heat pump, CO Ph, depends on several factors. Especially the temperature difference between waste heat source and potential user is an important factor. The temperature difference between condensation and evaporation temperature mainly determines the efficiency: the smaller the difference, the higher the CO Ph. The figure on the left shows the influence of this temperature difference on the CO Ph value. These values are based on figures from a Grasso 65HP compressor with the refrigerant Ammonia. The figure shows an increase in CO Ph with an increasing evaporation temperature. Furthermore it shows a decrease in CO Ph with a decreasing condensation temperature. In general the CO Ph decreases with an increase in temperature difference between condensation and evaporation. The figure below gives an indication of the dependence of the CO Ph of an Ammonia heat pump as a function of this temperature difference.
Remark:
Some of the articles are taken from the Internet. If there is any infringement, please contact us to delete it. If you’re interesting in heat pump products,please feel free to contact OSB heat pump.

