Another important factor that influences efficiency is the applied refrigerant. Ammonia, for example, is a very efficient refrigerant with a CO Ph of 6 for a evaporation temperature of 30 °C and condensation temperature of 70 °C. These same conditions only give a CO Ph of 4,5 for refrigerant R134A. Other factors that will affect the efficiency of a heat pump are system controls, efficiency of peripheral equipment like fans, pumps, etc.
Carnot efficiency
The theoretical maximum efficiency of a heat pump is described by the Carnot-efficiency:
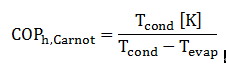
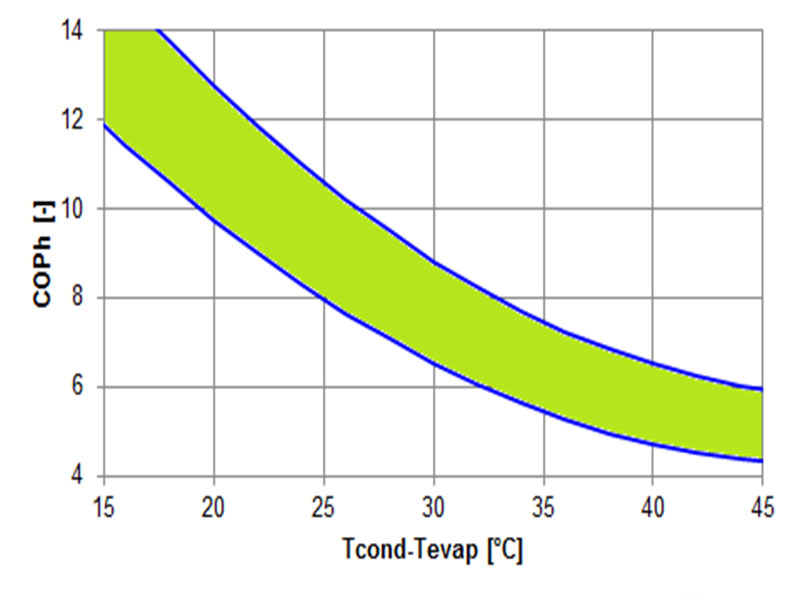
The equation shows that the Carnot-efficiency depends on the condensation and evaporation temperature. With an ideal compression cycle without losses it is possible to achieve the Carnot efficiency. However, in practice there are a lot of parameters that have a negative influence on the efficiency. Therefore the real CO Ph is given by the product of the Carnot efficiency and the system efficiency:
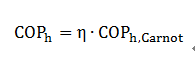
The system efficiency is usually 50% to 70%.
Lorentz efficiency
With a transcritical heat pump the Carnot-efficiency can not be used, because there is no condensation temperature, but a temperature range in the gas cooler. The theoretic maximum efficiency of a transcritical heat pump is described by the Lorentz efficiency.
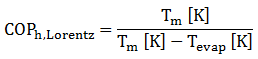
Tm is the mean temperature in the gas cooler. This temperature is calculated from the temperature at the inlet and the outlet of the gas cooler:
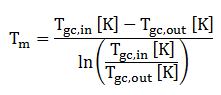
Similar to Carnot, the Lorentz efficiency will not be reached in practice due to all kind of losses. To determine the real COP, a system efficiency must be taken into account:
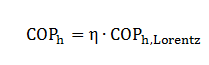
Remark:
Some of the articles are taken from the Internet. If there is any infringement, please contact us to delete it. If you’re interesting in heat pump products,please feel free to contact OSB heat pump. We are your best choice.

