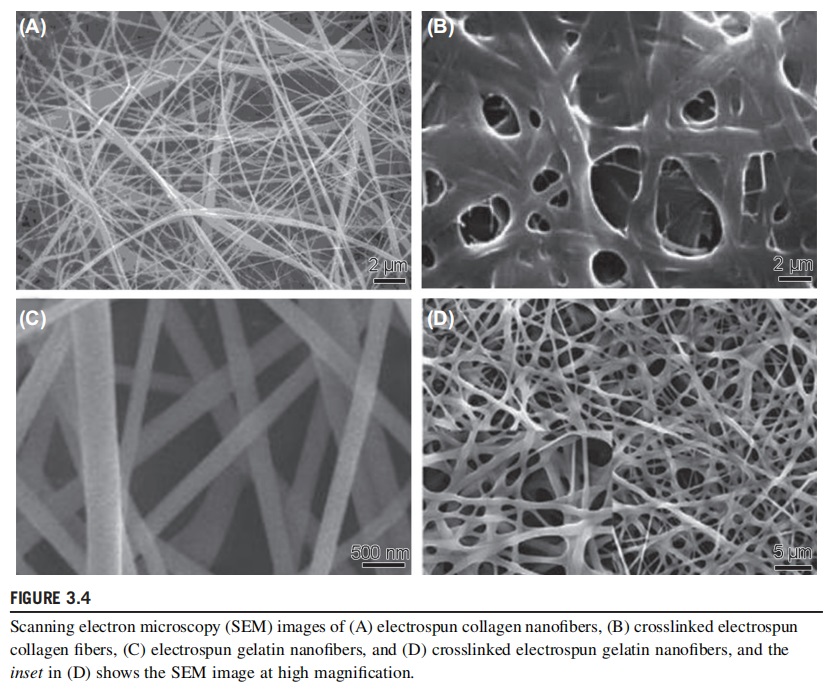
Gelatin is a kind of protein derived from the hydrolysis of collagen, which possesses composition as well as properties similar to those of collagen. Considering that gelatin aqueous solution easily forms a gel, water was generally not used as a solvent for electrospinning in the early years. Huang et al. (2004) utilized 2,2,2-trifluoroethanol as a solvent to prepare pristine gelatin nanofibers with good morphology. Gelatin/PCL nanofibers have also been prepared via a similar electrospinning process (Zhang et al., 2005; Strobel et al., 2017). In 2006, Li et al. (2006b) successfully prepared uniform electrospun gelatin nanofibers from aqueous solution by controlling the temperature of the solvent and environment (Fig. 3.4C), which not only realized the blending of gelatin with other water-soluble biomolecules, but also dramatically increased the potential application of electrospun gelatin nano-fibers in biomedicine. Crosslinked electrospun gelatin nanofibers have been prepared to enhance their mechanical properties for practical applications (Fig. 3.4D) (Zhang et al., 2006). Similarly, diverse functionalized electrospun gelatin nanocomposites have been developed as well (Salifu et al., 2017; Marino et al., 2017).

