Air source heat pump heating design and construction guide Chapter 1 The fifth chapter of the basic knowledge of air source heat pump, heating system design estimation index
In the program stage, the heating heat load can be estimated according to the thermal index. The area heat index is introduced below.
Thermal index per unit area: that is, the heating heat load equivalent to the floor area per square meter. Some commonly used heating heat indicators are listed below. In the table, the recommended values of heating heat indicators are given by building type and distinguishing between energy-saving buildings and non-energy-saving buildings. Energy-efficient buildings are relative to the buildings of the 1980s. According to the basic goal of building energy-saving development in China: the new heating residential building has been generally reduced by 30% from the local general design energy consumption level from 1980 to 1981, which is the first stage; since 1996, it has reached the requirements of the first stage. On the basis of energy saving 30%, (ie total energy saving 50%) is the second stage; from 2005 on the basis of the second stage requirements to save energy by 30% (that is, total energy saving 65%) is the third stage.
Therefore, when we use the thermal index, we should pay attention to the structure of the envelope structure, pay attention to whether the building is an energy-saving building, and know its construction age to judge its energy-saving degree, so that the estimation result is closer to the real energy consumption. For example, we can observe whether the window glass is hollow, aluminum alloy steel or broken bridge aluminum; steel nails can also be used to pierce the external wall insulation, and the thickness of the insulation layer is measured to roughly judge the energy saving situation. Common insulation layers are 30mm, 50mm, 80mm, etc.
The following table is quoted from "Code for Design of Urban Heating Pipe Network" CJJ34-2010. Central heating areas (Northeast, North China, Northwest) are generally considered for continuous heating. When used in the south, continuous heating can be used as reference. For intermittent heating, it should be converted according to heat balance. That is, intermittent heat index = continuous heat index × 24 / day heating hours. The residential units here refer to unit-type multi-storey houses. In the rural self-built houses, it is generally recommended to refer to single-storey buildings such as canteens, restaurants, and auditoriums. The upper area is smaller and the upper limit is larger.
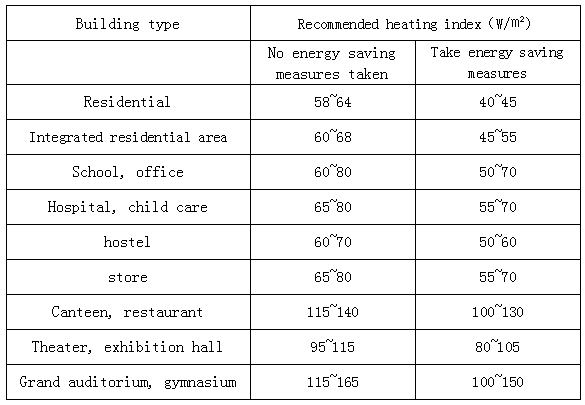
Applicable to the estimation of the overall energy consumption of the building in the absence of basic data. For example, the initial pipe diameter and the selection of the unit selection; the heat index is used in a single room, and the error may be large. When conditions permit, the building should be calculated on a case-by-case basis.

