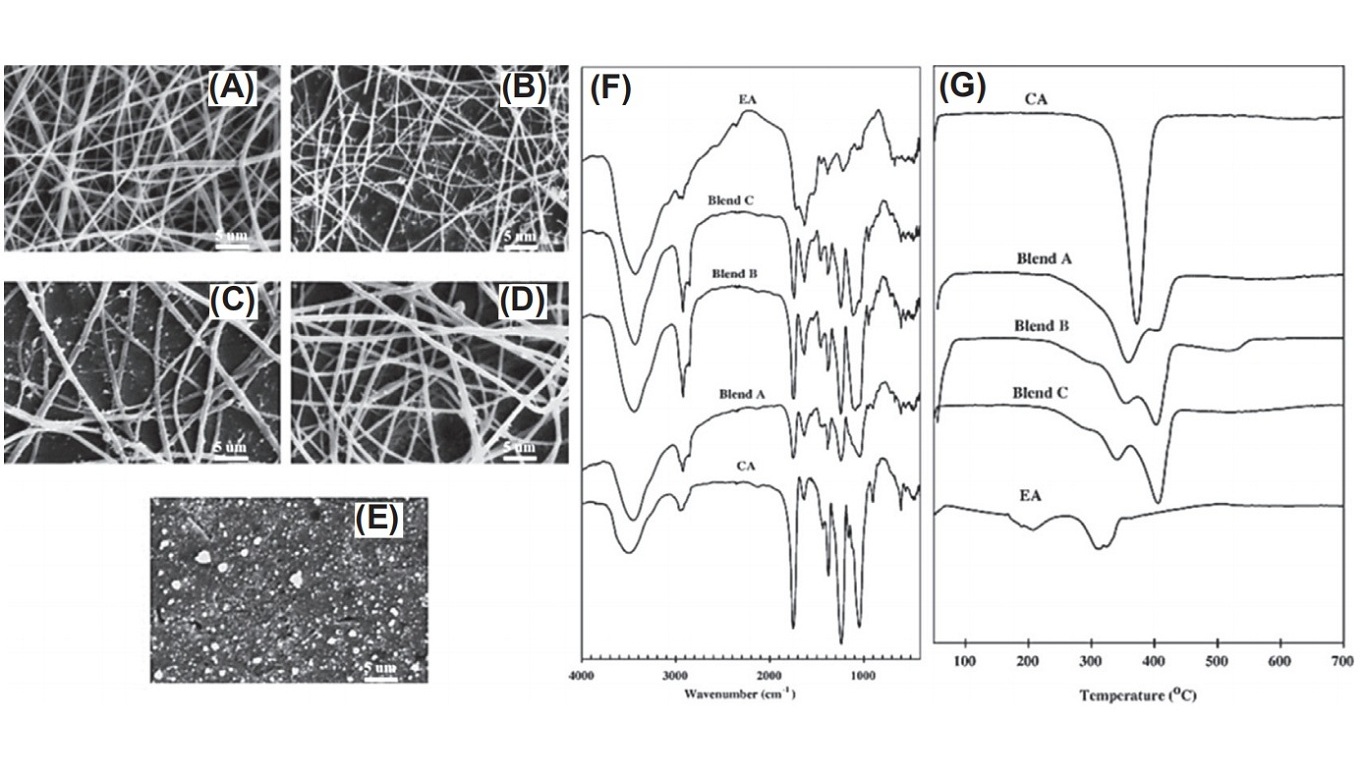
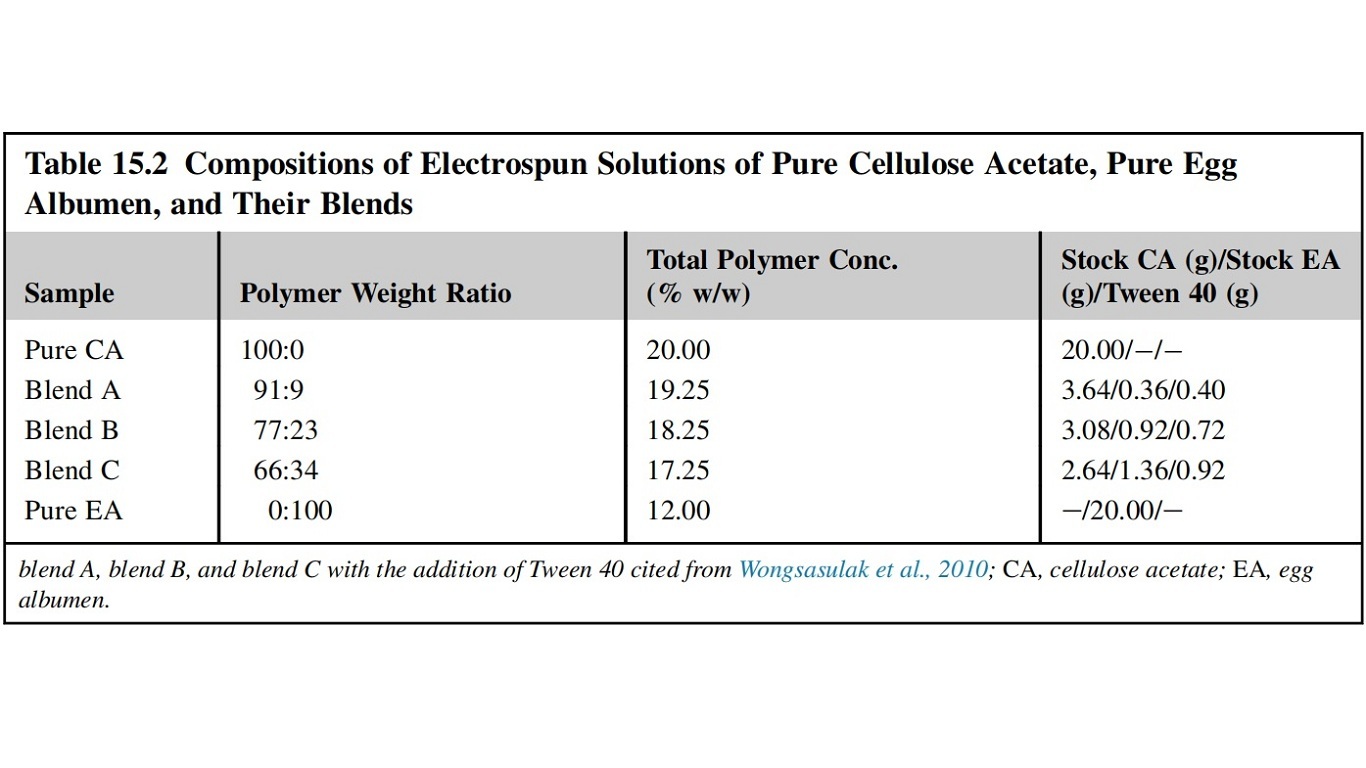
A study has reported the fabrication of electrospun edible nanofibrous films from a blended solution of CA and egg albumen (EA) (Figure; Table ). The solvents are 85% acetic acid for the CA and 50% formic acid for the EA. Tween 40 is added as a food-grade nonionic surfactant to modulate the solution properties.
To fabricate fibers with antimicrobial activity, Son et al. have reported the addition of silver nitrate into 10 wt% CA solution dissolved with a mixture of acetone and water (4:1). Afterward, the as-prepared fibers are treated by photoreduction, thereby converting the silver ions into silver nanoparticles with antimicrobial activity. And then the silver nanoparticles diffuse to the surface of the nanofibers to form aggregates, which inhibited the growth of various foodborne pathogens, including Staphylococcus aureus, Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumonia, and Pseudomonas aeruginosa.