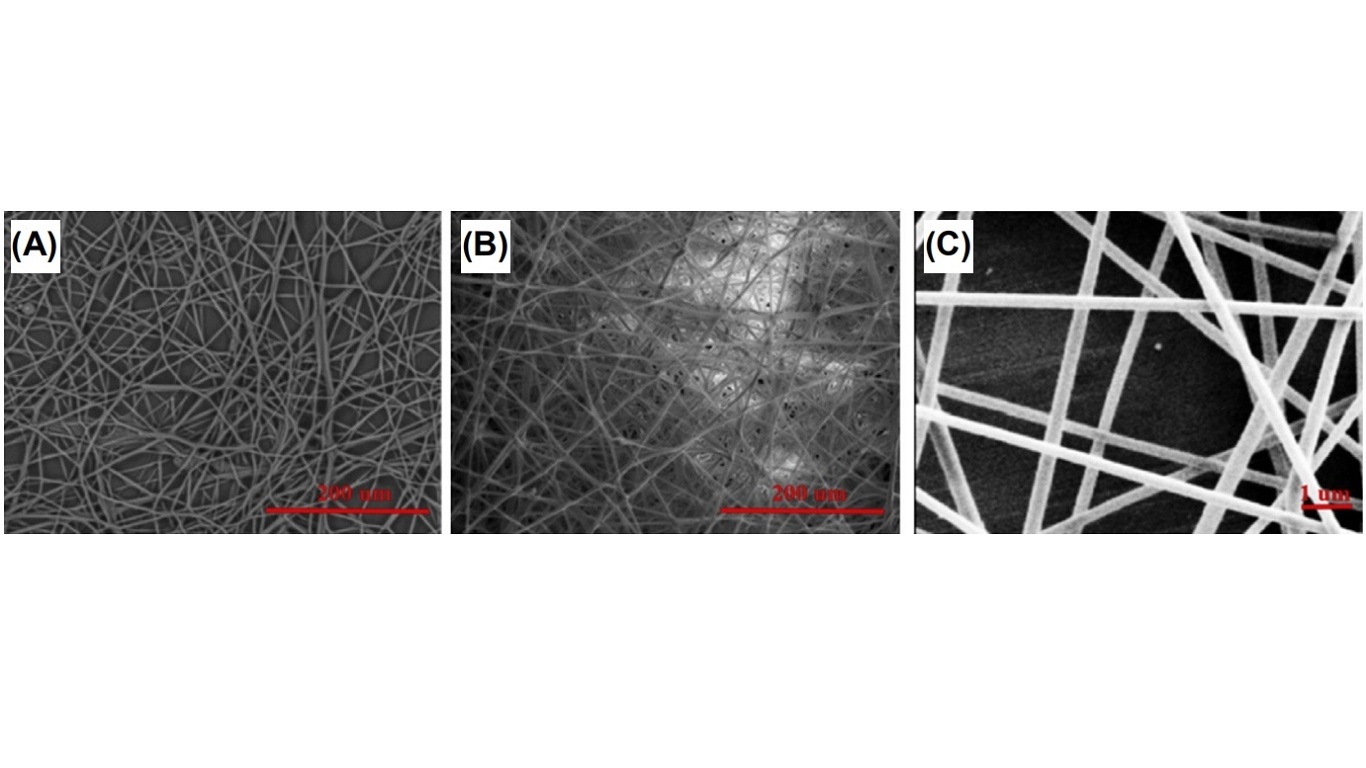
The obtained as-spun starch fibers (Fig. A) could be used in the food industry.
Electrospun nanofibers have been fabricated from high-amylose starch blended respectively with palmitic acid, ascorbyl palmitate, and cetyltrimethylammonium bromide (CTAB). Ascorbyl palmitate is a food additive source of vitamin C and an antioxidant. CTAB is an effective antiseptic agent against bacteria and fungi. The obtained inclusion complexes (Fig. B) provide a novel medium to encapsulate varied guest compounds, which expands the application of starch-based nanofibrous mats.
The Wang group has reported electrospun nanofibers of PVA and oxidized starch (Fig. C). Oxidized starch is a kind of cationic polysaccharide, which is ionized under acidic and neutral conditions. The addition of oxidized starch affects the conductivity of the solution, and the diameter of the fiber decreases upon the increase in the conductivity of the solution.