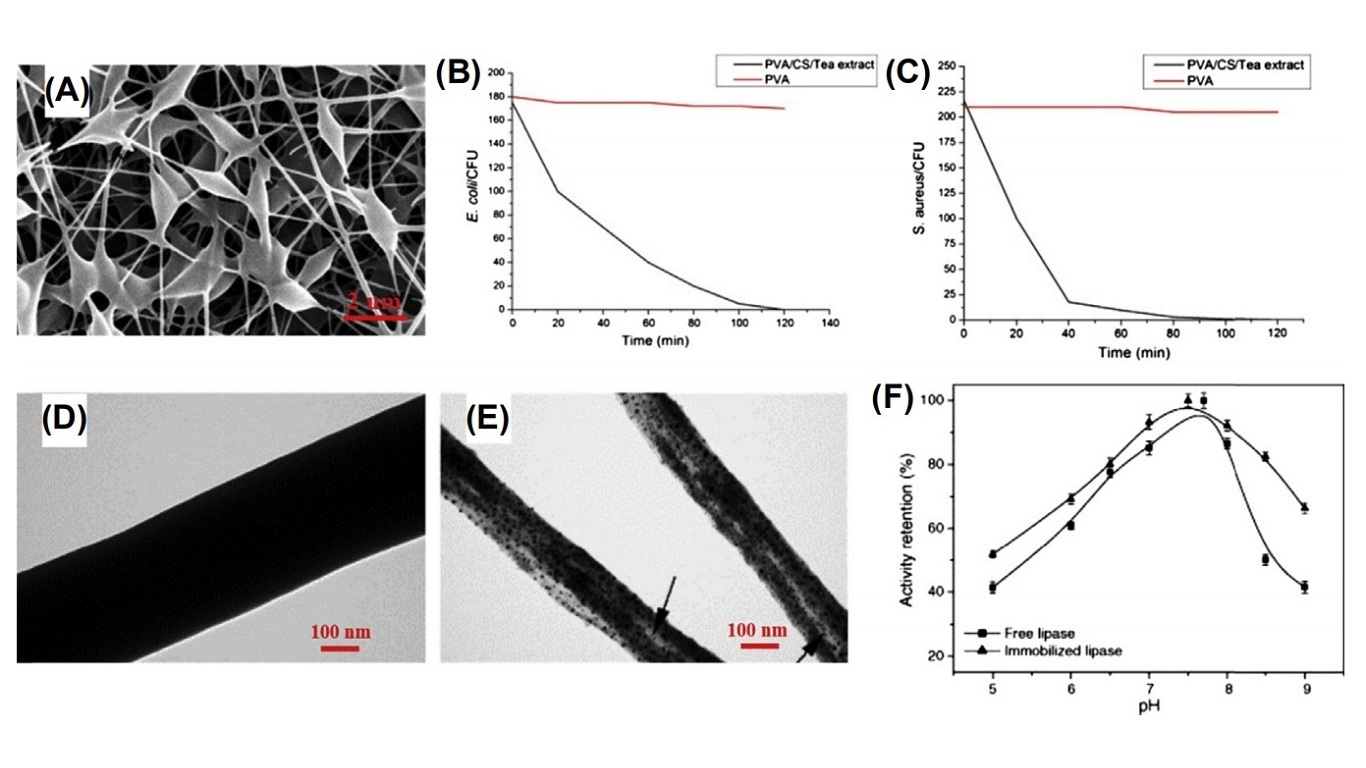
Glucose oxidase (GOD) is a promising material for food packaging and storage, due to the properties of deoxidation. Electrospun composite nanofibers of chitosan and polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) have been fabricated, on which GOD is deposited to detect glucose. Chitosan and PVA are mixed to fabricate electrospun mats with antimicrobial activity, as shown in Fig. 15.1. Further immobilization of GOD onto the mats exhibits long-term stability, good reproducibility, and absence of interference from other coexisting electroactive species for glucose detection. The obtained electrospun membranes show 73% deoxidization for the tested sample of jelly and cream cakes. However, the composite nanofibers have less efficacy in the preservation of sugar-rich or semisolid food. Similarly, studies have reported that immobilization of lipase onto chitosan and PVA nanofibrous membranes enhances the storage stability. Antimicrobial nanofibers prepared by electrospinning of TFA-dissolved chitosan are accepted as food contact materials with specific migration limits.