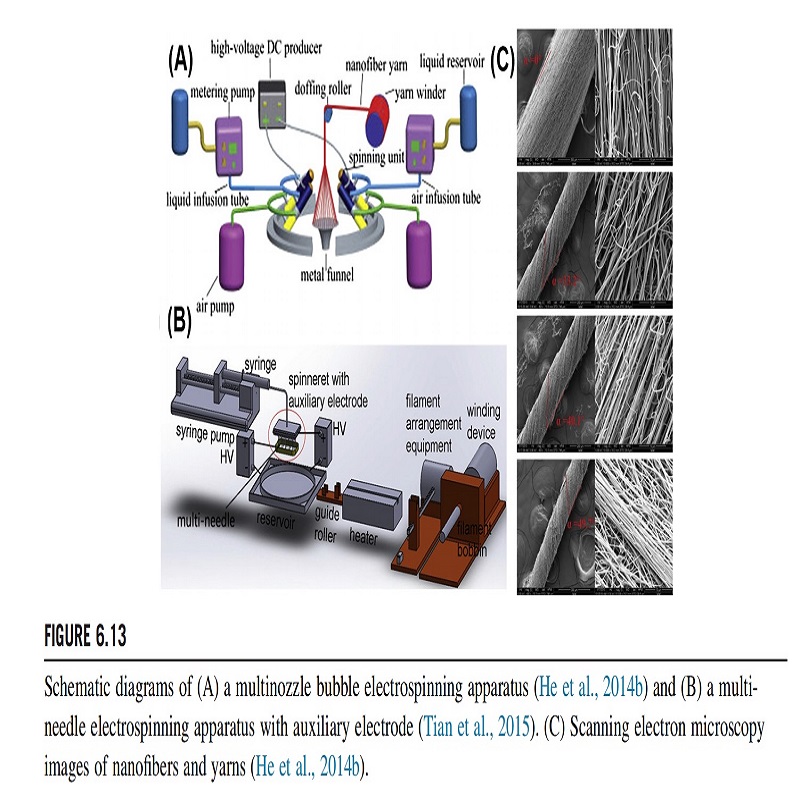
Multineedle Electrospinning Apparatus
Nanofiber yarn is defined as a twisted nanofiber bundle or tow featuring a morphology that is similar to filament yarn or spun yarn. Nanofiber yarn is mechanically suitable for weaving, knitting, and other methods used to produce fabrics. He and colleagues succeeded in producing continuous and twisted polyacrylonitrile nanofiber yarns by using a four-nozzle bubble electrospinning method, and the twist of the prepared nanofiber yarn could be adjusted by controlling the rotational speed of the collecting device, as shown in Fig. 6.13A and C. Two pairs of nozzles were positively and negatively charged, and the metal funnel collector was not grounded. After voltage was applied, the conjugate electric field came into being between the positive and the negative nozzles; however, the metal funnel located in the middle of the two groups of nozzles would have charges that were opposite those of the nearby charged nozzles. Therefore, induction fields were created between both edges of the funnel and their nearby charged nozzles. The electronic field lines were mainly distributed between the positive and the negative nozzles, and between the nozzles and the edge of the funnel. Because of the electrostatic induction effect, the charged jets ejected from two pairs of oppositely charged nozzles would be attracted toward the side of the inductive funnel with opposing charges. Next, the jets would become neutralized and form a hollow nanofiber web composed of nanofibers from positive and negative nozzles, and their edges would connect to the end of the funnel. After being drawn by an insulating rod placed near the central area of the funnel, the hollow nanofiber web formed a fibrous cone whose apex attached to the rod. Further drafting of the cone apex would induce the formation of oriented fiber bundles; the bundles were then twisted by rotating the funnel and wound onto the winder as continuous yarns. Lin, Dabirian, He, and coworkers developed another method to fabricate nanofiber yarn. This method applies opposing voltages to two groups of traditional needles in opposite arrangements, and then the nanofibers prepared from the two groups of needles with opposite charges are attracted and neutralized on a metal collector (such as a metal disk, cone, or funnel) in the middle of the two groups of needles. Finally, the gathered nanofibers are twisted by the rotation of the metal collector to obtain a continuous nanofiber yarn. Pan and colleagues used a multineedle electrospinning system to provide the nanofibers, and the electric field interference between the multineedle electrodes could be weakened by installing an auxiliary electrode around the needles. This made the jet have less offset during the electrospinning process and weakened the instability of the Taylor cone formation and the jet movement. Finally, the fabricated nanofibers were deposited in a liquid coagulation bath, and then continuous nanofiber filaments were obtained by drawing the collected nanofibers from the bath. The nanofiber yarns that can be processed by textile technology were obtained by mechanically combining and twisting several nanofiber filaments (Fig. 6.13B).

