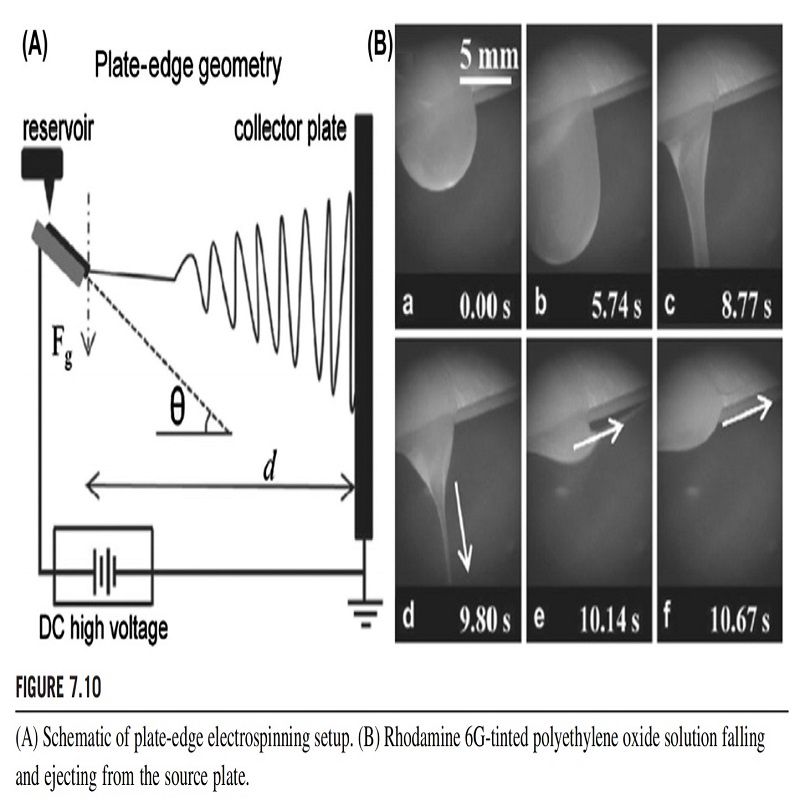
PLATE EDGE
In another setup reported by Thoppey et al., a plate at a certain horizontal angle was used for retaining the spinning solution, and nanofibers were generated from the plate edge (Fig. 7.10). An electrically insulated reservoir connected with one or more plastic pipettes was used to provide polymer solution to the plate, wherein each pipette formed a solution stream as a jet initiation site. Because of the high viscoelasticity, the polymer solution maintained its fluid shape. When it reached the plate edge, it formed a neck and became elongated. Under the influence of a strong applied electric field at the plate edge, jet initiation occurred. The production rate of this electrospinning was over five times higher than that of conventional needle electrospinning, even if using a single spinning site (one pipette). Nanofibers produced by this method had the same quality as those produced by conventional needle electrospinning under the same working conditions.

