A variety of refrigerants are available for usage in mechanical heat pumps. With each of them having their own advantages and disadvantages the choice of refrigerant depends on several criteria.
Selection criteria
In general the following criteria must be taken into account:
Pressure: At a given temperature the condensation pressure is different for different refrigerants. For certain refrigerants at high temperatures, pressure will become too high and normal heat pump components can no longer be applied. Low pressure is another risk: for low pressures the volume that needs to be swept increases. This requires larger components and thus an increase in investments. The figure below shows the temperature of evaporation as a function of pressure for several commonly used refrigerants.
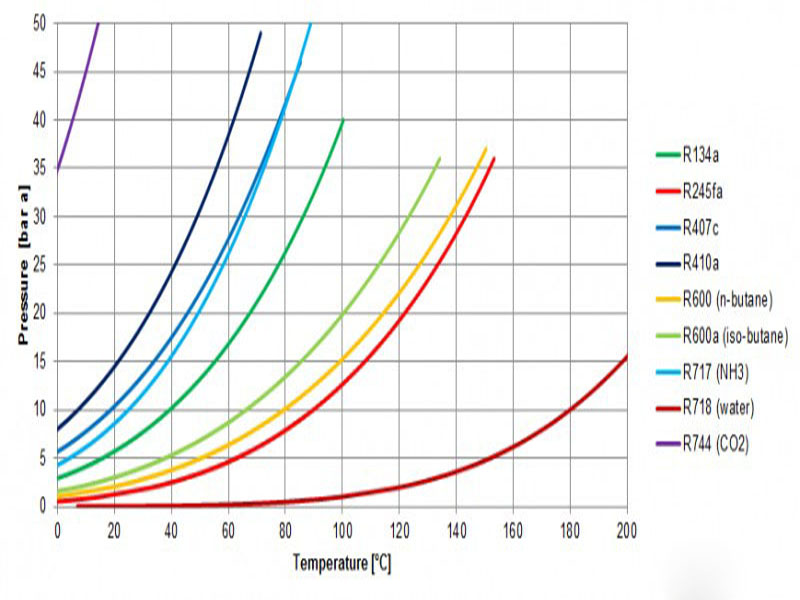
Critical temperature: Above a certain temperature a refrigerant reaches its supercritical area. Within the supercritical range the fluid and gaseous phase of the refrigerant can no longer be distinquished.
Energy efficiency: The efficiency of a heat pump depends on the choice of refrigerant.
Natural versus synthetic refrigerants: Most synthetic refrigerants (HFC's) contribute strongly to the greenhouse effect in case of leakage. This impact can be 3000 times higher as compared to CO2.
Besides the criteria mentioned above, several other factors are also involved in decision making. Investment costs, required size of the installation and safety and permits have to be taken into account when deciding what refrigerant to use.
Refrigerant tags
All refrigerants are denoted by a code. The code is started by a letter 'R' (Refrigerant) and followed by a number. From this number the following properties can be deduced:
R000-R399: Chemical refrigerants of which the composition is determined by their code number. General code: Rxyz= R(number of C atoms-1)(number of H atoms -1)(number of F atoms). R134, for example, consists of two C atoms, 4 H atoms and 4 F atoms: C2H2F4.
Remark:
Some of the articles are taken from the Internet. If there is any infringement, please contact us to delete it. If you’re interesting in heat pump products,please feel free to contact OSB heat pump.

