What is a heat pump? This is a very common question for HVAC professionals, as heat pumps are an often misunderstood marvel of engineering and design. In the simplest sense, a heat pump “pumps heat” from one place to another, moving heat out of your home when you want it cooler, and pumping heat into your home when you want it warmer. How? Let’s look.
What Does a Heat Pump Do?
A heat pump is both a heating and cooling system, extracting heat from the air and moving it via an air handler to another location. In the summer months, a heat pump will extract heat from your inside air and relocate it outdoors, essentially cooling your home. In the winter months, a heat pump system will move heat energy from the outside air into your home. Fundamentally, a heat pump can extract heat from the air source and release it either inside or outside the home, depending on the season. The ability to either heat or cool a home, combined with the fact that it moves heat rather than creates heat, makes a heat pump an excellent option for consumers interested in energy efficiency and versatility.
COOLING MODE
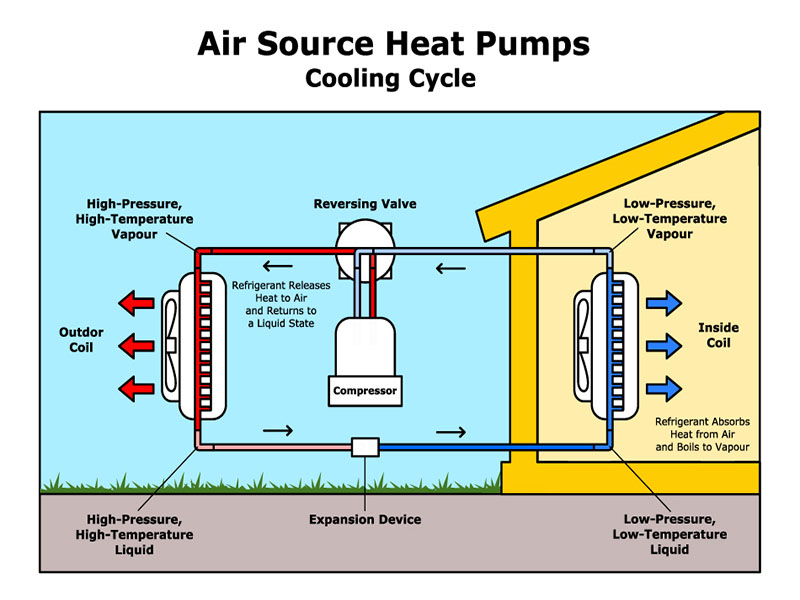
In cooling mode, a heat pump acts similar to a central air conditioner, cooling a home by absorbing heat energy inside the home and releasing it outside the home as a compressor circulates refrigerant between the indoor air handler unit and the outdoor compressor.
HEATING MODE
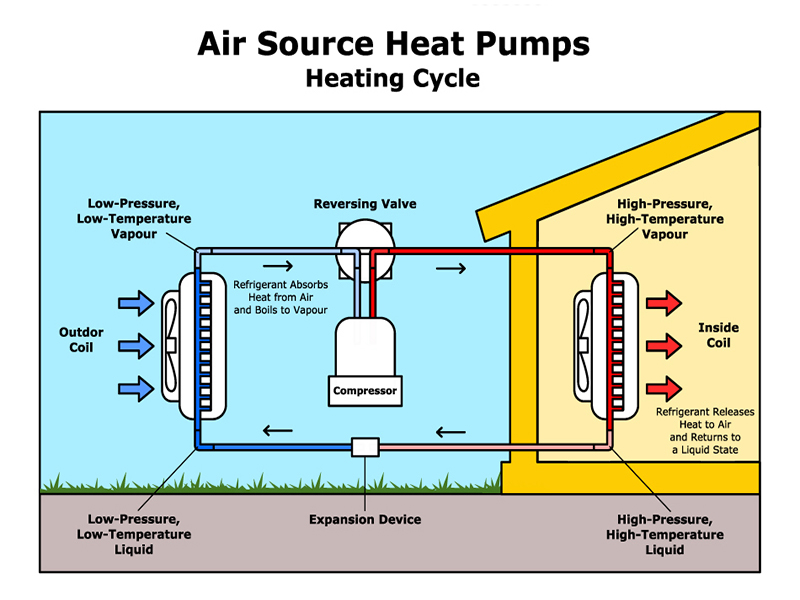
In heating mode, a reversing valve allows the heat pump system to operate as a heater, absorbing heat energy from the outside air and releasing it inside the home. Additionally, and especially useful in colder regions, heat pumps can be used in combination with oil or gas furnaces to create a powerful, energy efficient solution, resulting in significant savings on overall heating costs.
Types of Heat Pumps
The two most common types of heat pumps are air-source heat pumps and ground-source heat pumps. Air-source heat pumps are more popular for residential heating and cooling. They transfer heat between the air inside your house and the air outside your house. Ground-source heat pumps, sometimes called geothermal heat pumps, transfer heat between the air inside your home and the ground outside. These units are more expensive to install but are typically more efficient and have a lower operating cost due to the moderate temperate and consistency of the ground from one season to the next.
Where Do Heat Pumps Work Best?
Heat pumps work best in moderate climates, where the outside temperature during colder months does not drop near or below freezing on a regular basis. Although, as mentioned previously, a heat pump can be combined with an existing gas or oil furnace to create a solution. In this situation, the heat pump operates as the primary heating unit so long as it is more efficient than the gas/oil furnace. If the outside temperature drops too low for the heat pump to operate effectively and efficiently, the furnace will take over until outside temperature rises. The ability of a solution to switch between the heat pump and the furnace depending on conditions makes it an extremely energy efficient option with exceptional HSPF ratings, resulting in reduced energy consumption and costs.
Remark:
Some of the articles are taken from the Internet. If there is any infringement, please contact us to delete it. If you’re interesting in heat pump products,please feel free to contact OSB heat pump.

