First, the asynchronous variable frequency speed control motor is derived from the ordinary asynchronous motor. Because it has to adapt to the characteristics of the inverter output power, the motor has made great changes in the rotor slot type, insulation process, electromagnetic design check, etc., especially the motor. Ventilation and heat dissipation, it is usually added a separate forced cooling fan to adapt to the efficient heat dissipation of the motor at low speed and reduce the wind consumption of the motor at high speed.
The output of the inverter generally shows the output frequency of the power supply. The output of the speed is displayed as the calculated number of poles of the motor and the output frequency of the power supply. It is very different from the actual speed of the asynchronous motor. When using a general asynchronous variable frequency motor, the rotation of the asynchronous motor The difference is determined by the manufacturing process of the motor, so the dispersion is very large, and the change of the load directly affects the rotational speed of the motor. To accurately control the rotational speed of the motor, only the photoelectric encoder can be used for closed-loop control, and the accuracy of the rotational speed when the single machine is controlled. It is determined by the number of pulses of the encoder. When multi-machine control, the speed of multiple motors cannot be strictly synchronized. This is determined by the asynchronous motor.
Second, the synchronous variable frequency speed control motor has a permanent magnet embedded in the rotor. When the motor is started instantaneously, the motor is turned into normal operation, and the rotating magnetic field of the stator drives the rotor with the permanent magnet to perform synchronous operation. At this time, the speed of the motor is based on the motor. The pole number and the motor input power frequency form a strict correspondence, and the speed is not affected by the load and other factors.
The same synchronous variable frequency motor also adds a separate forced cooling fan to accommodate the efficient heat dissipation of the motor at low speeds and reduce the wind consumption of the motor at high speeds.
Due to the strict correspondence between the motor speed and the power frequency, the motor speed accuracy is mainly determined by the accuracy of the inverter output power frequency. The control system is simple, and the speed of multiple motors is controlled by controlling one motor for one inverter. There is also no need for expensive optical encoders for closed loop control.
Motor operating conditions
1. The altitude does not exceed 1000 meters.
When the altitude of the operating site is specified to exceed 1000 meters or the temperature of the cooling medium drops as the altitude increases, the temperature rise limit of the motor should be corrected.
2, the ambient temperature
The maximum ambient air temperature varies with the season, but does not exceed 40 °C. When the maximum ambient temperature at the operating location is above or below 40 °C, the motor temperature rise should be corrected.
The minimum ambient air temperature is -15 °C. However, the minimum ambient temperature for motors with power less than 600W (or VA) and with commutators or plain bearings is 5 °C. For motors with water as the cooling medium, the minimum temperature of water and ambient air is 5 °C.
3, the relative humidity of the ambient air
The wettest month and month average maximum relative humidity of the operation site is 90%, and the monthly average minimum temperature is not higher than 25 °C.
4. Electrical conditions:
Power supply: The AC motor should be suitable for three-phase 50Hz power supply.
Waveform and symmetry of voltage and current: The AC motor's power supply voltage is the actual sinusoidal waveform. For multiphase motors, it should also be the actual balance system.
When the motor voltage (if the AC power supply, the frequency is rated) varies between 95% and 105% of the rated value, the output power should still maintain the rated value. When the voltage changes as described above, the performance of the motor is allowed to differ from the standard specification, but when the voltage changes to the above limit and the motor is continuously operated, the maximum allowable temperature rise limit is:
Motors with rated power of 1000KW (or KVA) and below -10K;
Motors with rated power of 1000KW (or KVA) and above -5K;
5, the frequency of the power supply
When the frequency of the AC motor (voltage is rated) and the rated value does not exceed ±1%, the output power should still maintain the rated value. The voltage and frequency change simultaneously (both changes do not exceed ±5% and ±1%, respectively). If the changes are positive, the sum of the two does not exceed 6%; or both changes are negative or respectively For positive and negative values, the sum of the absolute values of the two does not exceed 5%, the AC motor output power can still maintain the rated value.
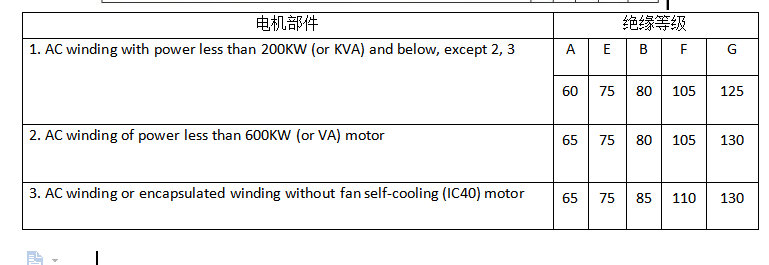
6, the temperature rise of the motor:
When the air-cooled motor is operated at rated power at an altitude not exceeding 1000 m and the ambient temperature does not exceed 40 ° C, the temperature rise limit from the ambient air temperature at the operating site is specified as follows: