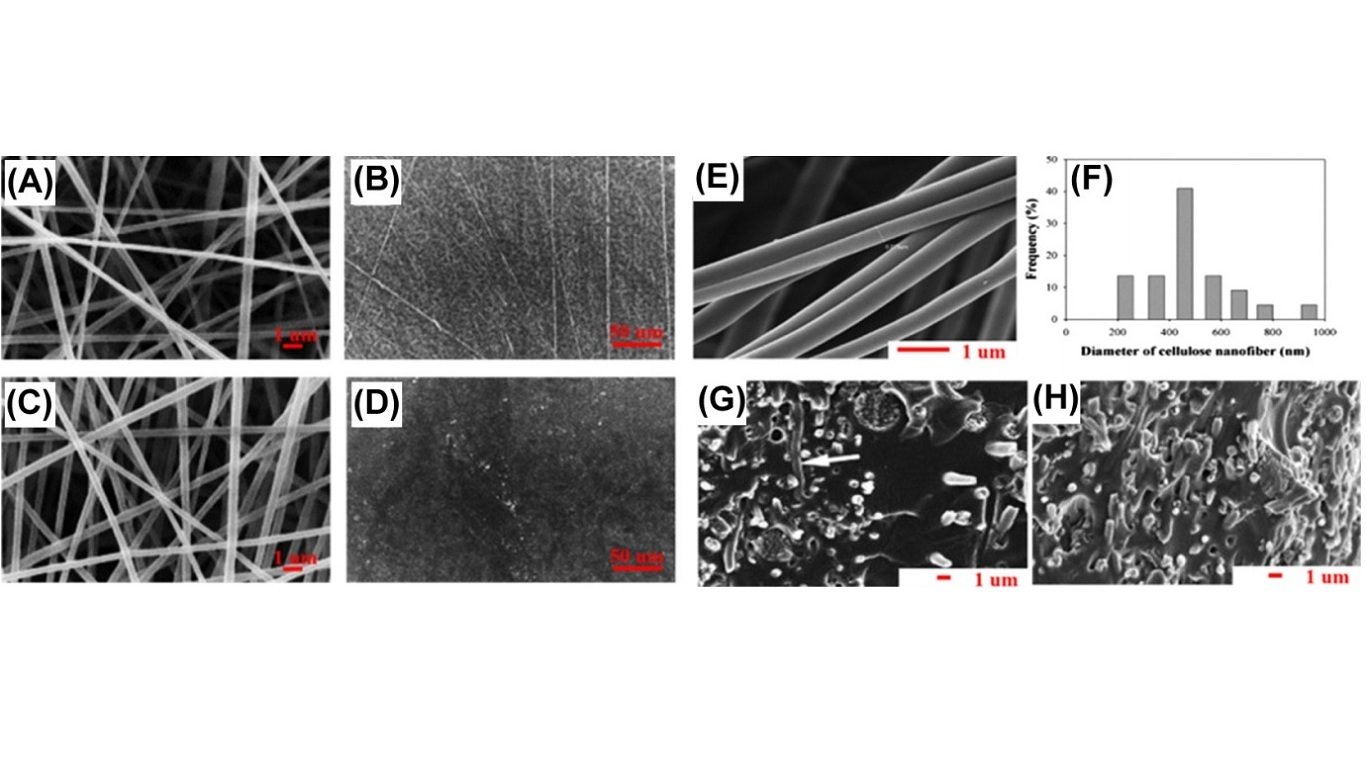
CA (low molecular weight, 30 kDa) is able to be dissolved in a 2:1 (v/v) acetone: dimethylacetamide solvent to form a 17 wt% polymer solution. Curcumin is one of the meat colorants in the food industry and has been applied in a polymer solution at a concentration of 5-20 wt% to fabricate bioactive cellulose nanofibers via electrospinning (Fig. A-D).
Electrospun cellulose nanofibers containing 5% curcumin have an average diameter of 314 ± 60 nm, while nanofibers containing 20% curcumin have an average diameter of 340 ± 98 nm. The biological activity of curcumin is maintained after the electrospinning process.
Chen and Liu have found that a blend of soybean protein isolate matrix and cellulose enhances the mechanical strength and Young modulus of composite nanofibers (Fig. G and H). Azeredo has reported that the incorporation of cellulose enhances the tensile strength and Young modulus of mango-puree-based edible films, which also improves the water vapor barrier of the films. These studies expand the applications of nanofibers in the food packaging industry.
Moreover, cellulosic nanofibers can be applied as thickeners and texturizing agents for sauces, dairy products, beverages, and meat products. They can mask unpleasant flavors in food. With their good performance in thermal resistance, cellulosic nanofibers can be used as delivery systems to protect heat-sensitive bioactive ingredients.