Lipase is an enzyme widely used in the production of dairy products, bakeries, fats, and oils. The modification of polyethylene glycol diacyl chloride on the nanofiber surface provides more reactive sites for the lipase enzyme, and the immobilization process does not affect its activity.
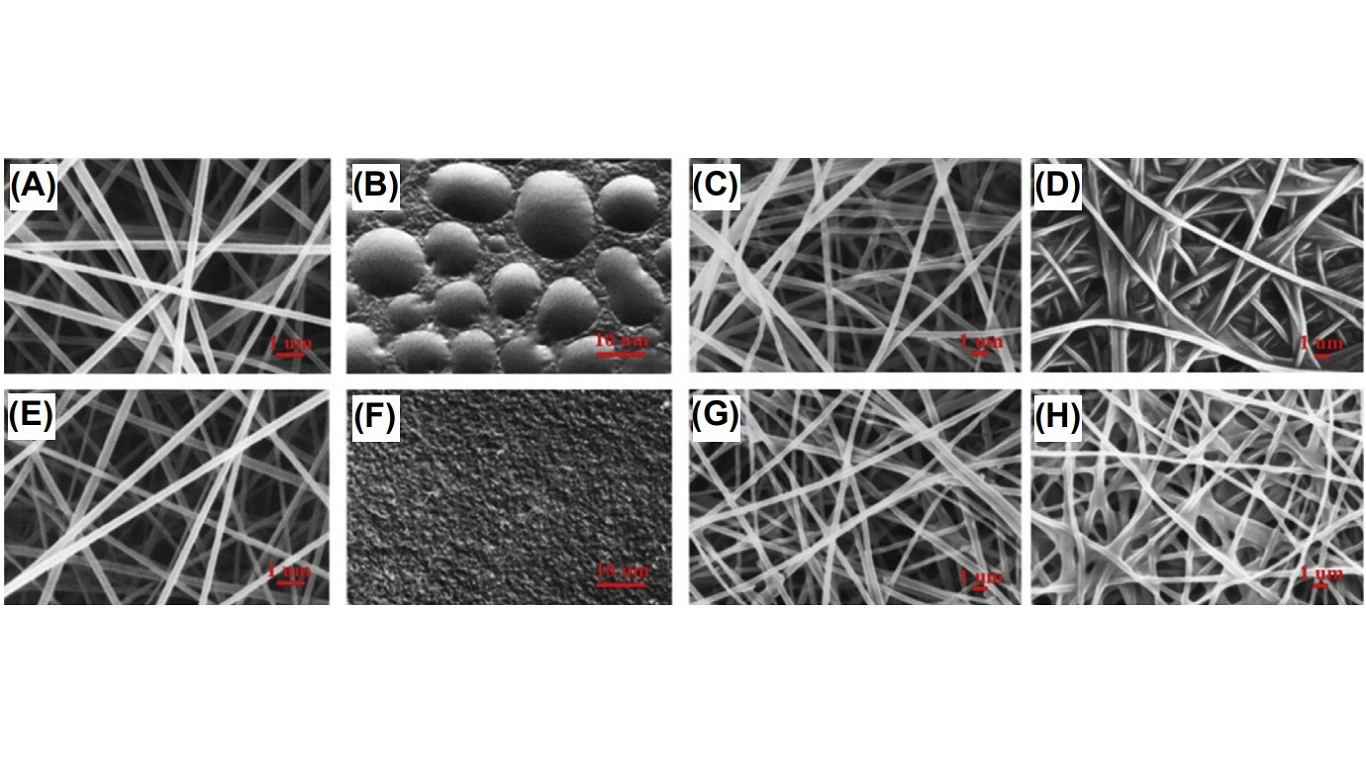
Cellulose acetate (CA) nanofibers with immobilization of vitamin A and E have an average diameter of 247-265 nm, with a smooth surface and round cross-section. The morphology of the loaded nanofibers is shown in Figure. Compared with the cast film of CA, the release of vitamins from electrospun nanofibers is sustained.