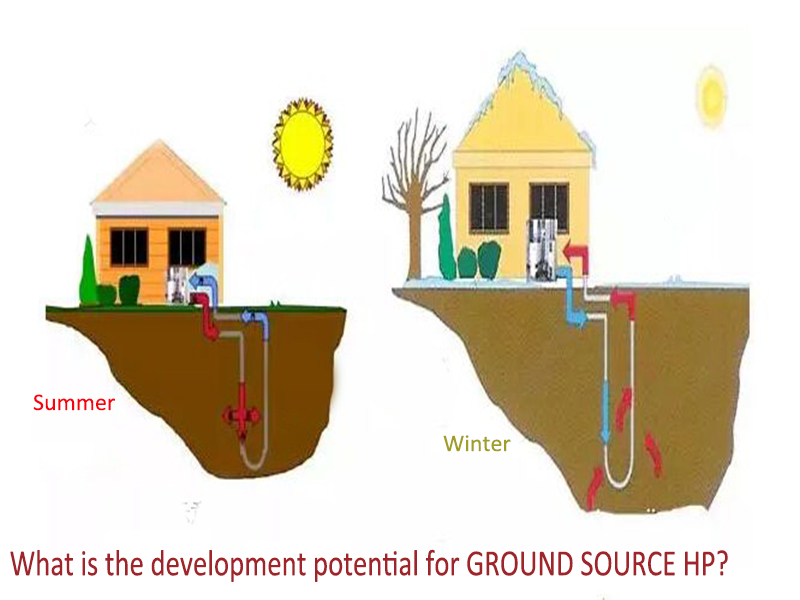
Ground source heat pump (GSHP) technology uses the relatively stable temperature characteristics of underground soil, surface water and groundwater to extract heat from low-level heat sources in winter and transfer heat to low-level heat sources in summer by consuming relatively high-quality energy to achieve heating or cooling purposes. Gound source heat pump (GSHP) does not need artificial cold and heat sources, and can replace traditional heating methods such like boilers and central air conditioning systems. At the same time, it can also provide domestic hot water. It is a new technology with high efficiency, energy saving and sustainable development.
Characteristics of Ground Source Heat Pump System (GSHP)
A. Green, environmentally friendly and pollution-free
Compared with air source heat pump, the pollutant emission of ground source heat pump can be reduced by more than 40%, and by more then 70% compared with electric heating. If combined with other energy-saving measures, the amount of energy saving and emission reduction will be more obvious. Ground source heat pump system (GSHP) does not need boilers and does not emit combustion products when heating in winter. It can greatly reduce the emissions of particulate matter and other pollutants and protect the environment.
B. high efficiency and energy saving, low energy utilization
The heat transfer efficiency of ground source heat pump system (GSHP) is very high due to the difference of heat dissipation between high temperature in summer and low temperature in winter. On the other hand, the shallow layer of the surface is a huge solar collector, which is not subject to geographical and resource constraints. This kind of energy, which is stored in the shallow layer of the earth’s surface and is similar to an infinite renewable and low energy source, can be exploited and utilized through the ground source heat pump system (GSHP).
C. good long-term economy
The initial investment cost of ground source heat pump system is higher than that of conventional coal-fired boiler heating system and cogeneration central heating system. However, this comparison does not calculate the investment of traditional heating and transportation infrastructure, nor does it quantify the cost savings of the ground source heat pump system, which can refrigerate, provide fresh air and hot water in addition to heating. Therefore, although the initial investment of ground source heat pump system is large, the operation and maintenance cost is low, and the incremental payback period of investment is about 4 to 10 years.

